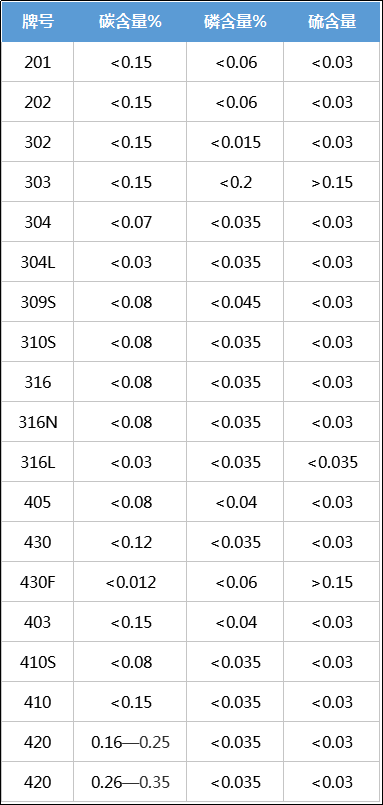
The sulfur content of steel shall not exceed 0.05%; the phosphorus content in general steel is limited to below 0.0%. Therefore, sulfur and phosphorus content is a very important indicator. Carbon structural steel and high-quality carbon structural steel are divided according to it: steel with sulfur and phosphorus content not exceeding 0.04% is called high-quality steel; steel with sulfur content not exceeding 0.03% and phosphorus content not exceeding 0.035% is called high-quality steel; steel with sulfur and phosphorus content not exceeding 0.025% is called special quality steel. Common sulfur and phosphorus content of stainless steel
Xinfa CNC tools have the characteristics of good quality and low price. For details, please visit: CNC Tools Manufacturers – China CNC Tools Factory & Suppliers (xinfatools.com)
2. Common stainless steel models
Common stainless steel models are usually represented by digital symbols, including 200 series, 300 series, and 400 series. They are the American representation methods, such as 201, 202, 302, 303, 304, 316, 410, 420, 430, etc. China’s stainless steel models are represented by element symbols plus numbers, such as 1Cr18Ni9, 0Cr18Ni9, 00Cr18Ni9, 1Cr17, 3Cr13, 1Cr17Mn6Ni5N, etc. The numbers represent the corresponding element content. 200 series: chromium-nickel-manganese austenitic stainless steel 300 series: chromium-nickel austenitic stainless steel 301: Good ductility, used for molded products. It can also be hardened by machine speed. Good weldability. Wear resistance and fatigue strength are better than 304 stainless steel. 302: Corrosion resistance is the same as 304, but the strength is better due to the relatively high carbon content. 302B: It is a stainless steel with a high silicon content, which has a high resistance to high temperature oxidation. 303: It is easier to process by adding a small amount of sulfur and phosphorus. 303Se: It is also used to make parts that require hot upsetting, because under such conditions, this stainless steel has good hot workability. 304: That is 18/8 stainless steel. The GB grade is 0Cr18Ni9. 309: It has better temperature resistance than 304.
304L: It is a variant of 304 stainless steel with a lower carbon content and is used in occasions where welding is required. The lower carbon content minimizes the precipitation of carbides in the heat-affected zone near the weld, and the precipitation of carbides may cause intergranular corrosion (welding corrosion) of stainless steel in certain environments.
304N: It is a nitrogen-containing stainless steel, and nitrogen is added to increase the strength of the steel.
305 and 384: They contain higher nickel and have a low work hardening rate, which is suitable for various occasions with high requirements for cold formability.
308: It is used to make welding rods.
309, 310, 314 and 330: The nickel and chromium content are relatively high, in order to improve the oxidation resistance and creep strength of steel at high temperatures. 30S5 and 310S are variants of 309 and 310 stainless steel, the only difference is that the carbon content is lower, in order to minimize the precipitation of carbides near the weld. 330 stainless steel has particularly high carburization resistance and thermal shock resistance.
316 and 317: Contain aluminum, so the pitting corrosion resistance in marine and chemical industrial environments is much better than 304 stainless steel. Among them, 316 stainless steel consists of variants including low-carbon stainless steel 316L, nitrogen-containing high-strength stainless steel 316N and free-cutting stainless steel 316F with a high sulfur content.
321, 347 and 348: They are stainless steels stabilized with titanium, niobium, tantalum and niobium respectively, suitable for welding components used at high temperatures. 348 is a stainless steel suitable for the nuclear power industry, and there are certain restrictions on the amount of tantalum and cobalt.
400 series: ferritic and martensitic stainless steels 408: good heat resistance, weak corrosion resistance, 11% Cr, 8% Ni 409: the cheapest model (UK and US), usually used as automobile exhaust pipes, ferritic stainless steel (chrome steel)
410: martensitic (high-strength chrome steel), good wear resistance, poor corrosion resistance.
416: the addition of sulfur improves the processing properties of the material.
420: “Tool-grade” martensitic steel, similar to Brinell high-chromium steel, the earliest stainless steel. Also used for surgical knives, can be made very bright
430: ferritic stainless steel, decorative, such as for car accessories. Good formability, but poor temperature resistance and corrosion resistance
440: high-strength tool steel, slightly higher carbon content, after proper heat treatment can obtain a higher yield strength, hardness can reach 58HRC, is one of the hardest stainless steels. The most common application example is “razor blades”. There are three commonly used models: 440A, 440B, 440C, and 440F (easy to process)
500 series: heat-resistant chromium alloy steel 600 series: martensitic precipitation hardening stainless steel 630: the most commonly used precipitation hardening stainless steel model, also commonly called 17-4; 17% Cr, 4% Ni
Post time: Nov-18-2024