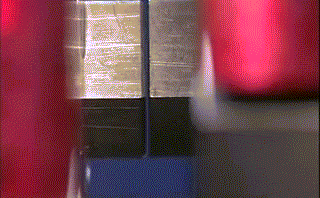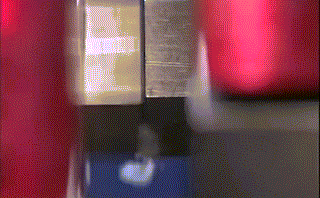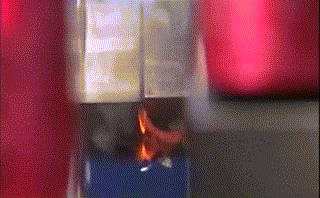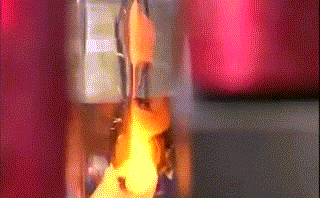
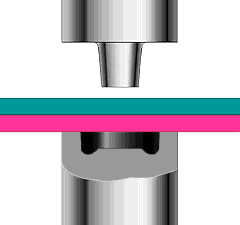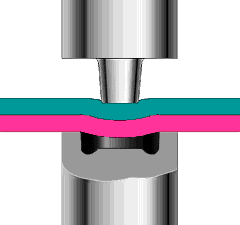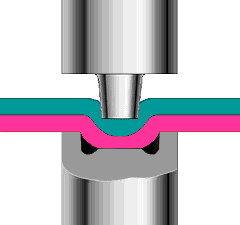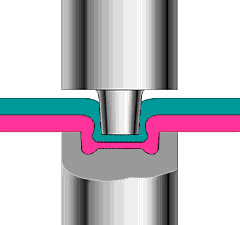
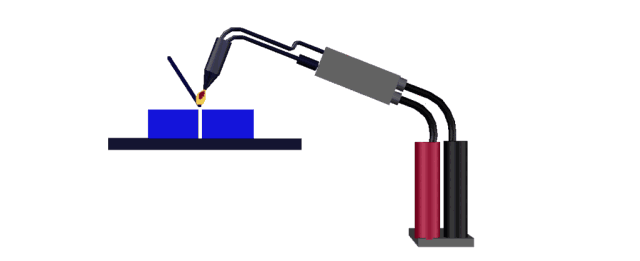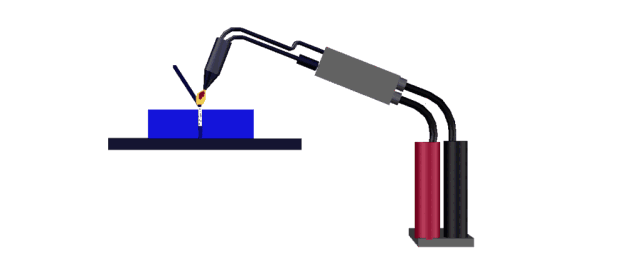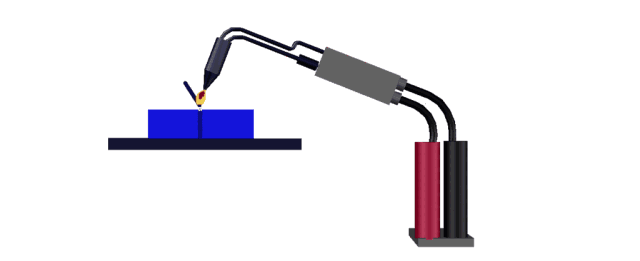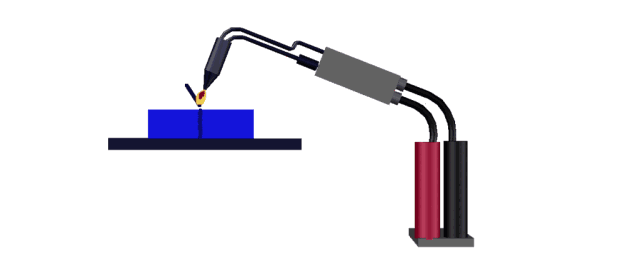
Hot air welding is also called hot air welding. Compressed air or inert gas (usually nitrogen) is heated to the required temperature through the heater in the welding gun and sprayed onto the plastic surface and the welding strip, so that the two are melted and combined under low pressure.
Plastics that are sensitive to oxygen (such as polyphthalamide, etc.) should use inert gas as the heating medium, and other plastics generally use filtered air.
This method is often used for welding plastics such as polyvinyl chloride, polyethylene, polypropylene, polyoxymethylene, polystyrene, and carbonate.
2. Hot-press welding
Hot-press welding uses heating and pressure to press the metal wire and the metal welding area together.
The principle is to make the metal in the welding area plastically deformed by heating and pressure, and at the same time destroy the oxide layer on the pressure-welding interface, so that the pressure-welded metal wire and the metal contact surface reach the atomic gravitational range, thereby generating attraction between atoms and achieving the purpose of bonding.
3. Hot plate welding
Hot plate welding adopts a plate-drawing structure, and the heat of the heating plate machine is transferred to the welding surface of the upper and lower plastic heating parts by electric heating.
Make its surface melt, then quickly withdraw the heating plate machine, and the upper and lower heating parts are heated and the molten surfaces are fused, solidified, and combined into one.
The whole machine is in the form of a frame, consisting of three plates: an upper template, a lower template, and a hot template, and is equipped with a hot mold, upper and lower plastic cold molds, and the action mode is pneumatic control.
4. Ultrasonic metal welding
Use high-frequency vibration waves to transmit to the two metal surfaces to be welded, and under pressure, the two metal surfaces are rubbed against each other to form a fusion between the molecular layers.
Its advantages are speed, energy saving, high fusion strength, good conductivity, no sparks, and close to cold processing; its disadvantages are that the welded metal parts cannot be too thick (generally less than or equal to 5mm), the welding points cannot be too large, and pressure is required.
Xinfa welding equipment has the characteristics of high quality and low price. For details, please visit: Welding & Cutting Manufacturers – China Welding & Cutting Factory & Suppliers (xinfatools.com)
5. Laser welding
Laser welding is an efficient and precise welding method that uses a high-energy-density laser beam as a heat source. It is one of the important aspects of the application of laser material processing technology.
Generally, a continuous laser beam is used to complete the connection of materials. Its metallurgical physical process is very similar to electron beam welding, that is, the energy conversion mechanism is completed through the “key-hole” structure.
The equilibrium temperature in the cavity is about 2500 0C, and the heat is transferred from the outer wall of the high-temperature cavity to melt the metal surrounding the cavity.
The keyhole is filled with high-temperature steam generated by the continuous evaporation of the wall material under the irradiation of the beam. The beam continuously enters the keyhole, and the material outside the keyhole flows continuously. As the beam moves, the keyhole is always in a stable state of flow.
The molten metal fills the gap left after the keyhole is removed and condenses, and the weld is formed.
6. Brazing
Brazing is a welding method that heats the molten filler (brazing material) with a melting point lower than the workpiece to be connected to a temperature higher than the melting point to make it fluid enough, and uses capillary action to fully fill the space between the two workpieces (called wetting), and then joins the two after solidification. Traditionally in the United States, temperatures above 800 ° F (427 ° C) are called brazing (hard brazing), and vice versa.
Manual welding is a welding method that is operated by hand-held welding torches, welding guns or welding tongs.
7. Resistance welding
Resistance welding is a manufacturing process and technology that joins metals or other thermoplastic materials such as plastics by heating. It is a method of welding by applying pressure through electrodes after the workpieces are combined, and using the resistance heat generated by the current passing through the contact surface and adjacent areas of the joint.
Friction welding is a solid-phase welding method that uses mechanical energy as energy. It uses the heat generated by the friction between the end faces of the workpieces to make them reach a plastic state, and then forges them to complete the welding.
8. Electroslag welding
Electroslag welding uses the resistance heat generated by the current passing through the slag as a heat source to melt the filler metal and the base material, and after solidification, a firm connection between metal atoms is formed.
At the beginning of welding, the welding wire and the welding groove are short-circuited to start the arc, and a small amount of solid flux is continuously added. The heat of the arc is used to melt it to form liquid slag. When the slag reaches a certain depth, the feeding speed of the welding wire is increased, and the voltage is reduced, so that the welding wire is inserted into the slag pool, the arc is extinguished, and the electroslag welding process is turned on.
Electroslag welding mainly includes nozzle electroslag welding, non-nozzle electroslag welding, wire electrode electroslag welding, plate electrode electroslag welding, etc.
Its disadvantages are that the input heat is large, the joint stays at high temperature for a long time, the weld is easy to overheat, the weld metal is a coarse crystal cast structure, the impact toughness is low, and the weldment generally needs to be normalized and tempered after welding.
9. High-frequency welding
High-frequency welding (high-frequency welding) uses solid resistance heat as energy. During welding, the resistance heat generated by high-frequency current in the workpiece is used to heat the surface of the workpiece welding area to a molten or nearly plastic state, and then (or not) the upsetting force is applied to achieve the metal bonding.
10. Riveting
Riveting refers to the method of connecting two plates or objects together by drilling holes in their parts, then inserting rivets, and riveting the rivets with a rivet gun.
Hot melt is a type of connection that is made by heating the material to its (liquid) melting point.
Post time: Dec-09-2024