Summary and analysis of eight defects in welding
Quality defects in welding engineering mainly include the following aspects: All defects that can be seen by naked eyes or low-power magnifying glasses and are located on the surface of the weld, such as undercut (undercut), weld nodules, arc pits, surface pores, slag inclusions, surface cracks, unreasonable weld positions, etc. are called external defects, and internal pores, slag inclusions, internal cracks, incomplete penetration, and incomplete fusion that must be discovered by destructive tests or special non-destructive testing methods are called internal defects. However, the most common ones are not cleaning the welding slag and spatter after welding, and not cleaning the weld scar.
The weld size does not meet the specification requirements
Phenomenon: The height of the weld is too large or too small during the inspection; or the width of the weld is too wide or too narrow, and the transition between the weld and the base material is not smooth, the surface is rough, the weld is not neat in the longitudinal and transverse directions, and the concave amount of the weld in the corner weld is too large.
Reason: The straightness of the weld groove processing is poor, the angle of the groove is improper, or the assembly gap is uneven. The current is too large during welding, which makes the electrode melt too quickly and it is difficult to control the weld formation. The current is too small, which will cause the electrode to “stick” during welding arc initiation, resulting in incomplete welding or weld nodules. The welder is not skilled enough, the rod movement method is improper, such as too fast or too slow, and the welding rod angle is incorrect. In the submerged arc automatic welding process, the welding process parameters are improperly selected.
Prevention and control measures: Process the weld groove according to the design requirements and the provisions of the welding specifications. Try to use mechanical processing to make the groove angle and the straightness of the groove edge meet the requirements, and avoid using artificial gas cutting and manual scraping to process the groove. During the assembly, ensure the uniformity of the weld gap to lay the foundation for ensuring the welding quality. Select appropriate welding process parameters through welding process assessment. Welders must be certified before they can work, and trained welders have a certain theoretical foundation and operating skills. The last layer of multi-layer weld on the welding surface should be welded with a smaller current than the welding current between each layer and a small diameter (φ2.0mm~3.0mm) electrode for surface welding while ensuring fusion with the bottom layer. The rod conveying speed is required to be uniform, rhythmically advance longitudinally, and make a certain width of lateral swing to make the weld surface neat and beautiful.
Bite edge (bite meat)
Xinfa welding equipment has the characteristics of high quality and low price. For details, please visit: Welding & Cutting Manufacturers – China Welding & Cutting Factory & Suppliers (xinfatools.com)
Phenomenon: The depression or groove melted by the arc during welding is not supplemented by the molten metal, leaving a gap. Too deep an undercut will weaken the strength of the weld joint, causing local stress concentration, and cracks will be generated at the undercut after bearing.
Reason: The undercut is mainly caused by excessive welding current, too long arc, improper electrode angle control, improper electrode speed, and too short electrode retention length at the end of welding. It is generally a common defect in vertical welding, horizontal welding, and overhead welding.
Preventive measures: The current should not be too large during welding, the arc should not be too long or too short, and short arc welding should be used as much as possible. Master the appropriate electrode angle and skilled electrode movement techniques. When the electrode swings to the edge, it should be slightly slower so that the molten electrode metal fills the edge, and it should be slightly faster in the middle. The depth of the weld undercut should be less than 0.5mm, the length should be less than 10% of the total length of the weld, and the continuous length should be less than 10mm. Once the depth or thickness exceeds the above tolerance, the defect should be cleaned and filled with welding using a smaller diameter welding rod of the same brand and a welding current slightly higher than normal.
Crack
Phenomenon: During or after welding, metal cracks occur in the welding area. They occur inside or outside the weld, and may also occur in the heat-affected zone. According to the location of the cracks, they can be divided into longitudinal cracks, transverse cracks, arc crater cracks, root cracks, etc., and can also be divided into hot cracks, cold cracks and reheating cracks.
Cause: Large stress is generated after the heat-affected zone of the weld shrinks. The parent material contains more hardened structures and is prone to cracks after cooling. There is a relatively high concentration of hydrogen in the weld. And other harmful element impurities, etc., are prone to cold and hot cracks.
Prevention and control measures: Mainly start with stress elimination, correct use of welding materials and perfect operation process. Pay attention to the groove form of the welding joint to eliminate cracks caused by uneven heating and cooling of the weld due to thermal stress. For example, when welding steel plates of different thicknesses, the thick steel plate must be thinned. The selected materials must meet the requirements of the design drawings, strictly control the source of hydrogen, dry the welding rods before use, and carefully clean the oil, moisture and other impurities on the groove. During welding, select reasonable welding parameters to control the input heat between 800 and 3000℃ cooling temperature to improve the microstructure of the weld and heat-affected zone. When the welding environment temperature is low and the material is thin, in addition to increasing the operating environment temperature, it should also be preheated before welding. After welding, try to keep the temperature warm and perform post-weld heat treatment to eliminate delayed cracks caused by residual stress in the weld during the cooling process.
Arc crater
Phenomenon: The arc pit is a downward movement at the end of the weld, which not only weakens the weld strength, but also causes cracks during the cooling process.
Reason: The arc extinguishing time is too short at the end of welding, or the current used when welding thin plates is too large.
Preventive measures: When the weld is finished, make the electrode stay for a short time or make several circular movements. Do not stop the arc suddenly so that there is enough metal to fill the molten pool. Ensure appropriate current during welding, and add arc-starting plates to the main components to lead the arc pit out of the weldment.
Slag inclusion
Phenomenon: Non-metallic inclusions such as oxides, nitrides, sulfides, phosphides, etc. were found in the weld through non-destructive testing, forming a variety of irregular shapes, and the most common ones are cone-shaped, needle-shaped and other slag inclusions. Metal weld slag inclusions will reduce the plasticity and toughness of the metal structure, and will also increase stress, resulting in cold and hot brittleness, which will easily cause cracks and damage the components.
Reason: The weld parent material is not cleaned cleanly, the welding current is too small, the molten metal solidifies too quickly, and the slag has no time to float out.The chemical composition of the welding parent material and the welding rod is impure. If there are multiple components such as oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus, and silicon in the molten pool during welding, non-metallic slag inclusions are easily formed.The welder is not skilled in operation and the rod transportation method is improper, so that the slag and molten iron are mixed and inseparable, which hinders the slag from floating.The weld groove angle is small, and the electrode coating falls off in pieces and is not melted by the arc; during multi-layer welding, the slag is not cleaned cleanly, and the slag is not removed in time during operation, which are all causes of slag inclusion.
Preventive measures: Use electrodes with good welding process performance, and the welded steel must meet the requirements of the design documents. Select reasonable welding process parameters through welding process assessment. Pay attention to the cleaning of welding grooves and edge ranges, and the electrode groove should not be too small; for multi-layer welds, the welding slag of each layer of welds must be carefully removed. When using acid electrodes, the slag must be behind the molten pool; when using alkaline electrodes to weld vertical angle seams, in addition to correctly selecting the welding current, short arc welding must be used, and the electrode must be moved correctly to swing the electrode appropriately so that the slag floats to the surface. Use preheating before welding, heating during welding, and insulation after welding to allow it to cool slowly to reduce slag inclusions.
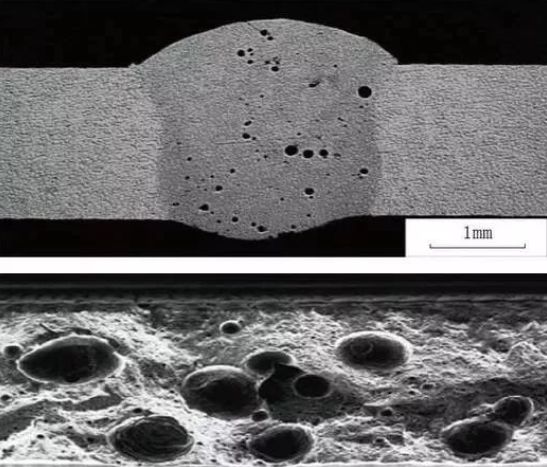
Porosity
Phenomenon: The gas absorbed in the molten weld metal during the welding process does not have time to be discharged from the molten pool before cooling, and remains inside the weld to form holes. According to the location of the pores, they can be divided into internal and external pores; according to the distribution and shape of the pore defects, the presence of pores in the weld will reduce the strength of the weld, and also produce stress concentration, increase low-temperature brittleness, thermal cracking tendency, etc.
Cause: The welding rod itself is inferior, the welding rod is damp and not dried according to the requirements; the welding rod coating is deteriorated or peeled off; the welding core is rusted, etc. There is residual gas in the smelting of the parent material; the welding rod and the weldment are stained with impurities such as rust and oil, and during the welding process, gas is generated due to high-temperature gasification. The welder is not skilled in operation technology, or has poor eyesight and cannot distinguish between molten iron and coating, so that the gas in the coating is mixed with the metal solution. The welding current is too large, which makes the welding rod red and reduces the protection effect; the arc length is too long; the power supply voltage fluctuates too much, causing the arc to burn unstably, etc.
Preventive measures: Use qualified welding rods. Do not use welding rods with cracked, peeled, deteriorated, eccentric or severely rusted coatings. Clean the oil stains and rust spots near the weld and on the surface of the welding rod. Choose the appropriate current and control the welding speed. Preheat the workpiece before welding. When welding is finished or paused, the arc should be withdrawn slowly, which is conducive to slowing down the cooling speed of the molten pool and the discharge of gas in the molten pool, avoiding the occurrence of pore defects. Reduce the humidity of the welding operation site and increase the temperature of the operating environment. When welding outdoors, if the wind speed reaches 8m/s, rain, dew, snow, etc., effective measures such as windbreaks and canopies should be taken before welding operations.
Failure to clean up spatter and welding slag after welding
Phenomenon: This is the most common common problem, which is not only unsightly but also very harmful. Fusible spatter will increase the hardened structure of the material surface, and easily produce defects such as hardening and local corrosion.
Reason: The medicine skin of the welding material is damp and deteriorated during storage, or the selected welding rod does not match the parent material. The selection of welding equipment does not meet the requirements, the AC and DC welding equipment do not match the welding material, the polarity connection method of the welding secondary line is incorrect, the welding current is large, the edge of the weld groove is contaminated with debris and oil stains, and the welding environment does not meet the welding requirements. The operator is not skilled and does not operate and protect according to the regulations.
Prevention and control measures: Select appropriate welding equipment according to the welding parent material. The welding rod must have a drying and constant temperature equipment, a dehumidifier and air conditioner in the drying room, and the distance from the ground and the wall should be no less than 300mm. Establish a system for receiving, sending, using, and keeping welding rods (especially for pressure vessels). Clean the edge of the weld to remove moisture, oil and rust. During the winter rainy season, a protective shed is overlapped to ensure the welding environment. Before welding nonferrous metals and stainless steel, protective coatings can be applied to the base metal on both sides of the weld for protection. Welding rods, thin-coated welding rods, and argon protection can also be used to eliminate spatter and reduce slag. Welding operations require timely cleaning of welding slag and protection.
Arc scar
Phenomenon: Due to careless operation, the welding rod or welding handle contacts the weldment, or the ground wire contacts the workpiece poorly, causing an arc for a short time, leaving arc scars on the workpiece surface.
Reason: The electric welding operator is careless and does not take protective measures and maintain the tools.
Preventive measures: Welders should regularly check the insulation of the welding handle wire and ground wire used, and wrap them in time if they are damaged. The ground wire should be installed firmly and reliably. Do not start an arc outside the weld when welding. The welding clamp should be placed in isolation from the parent material or hung appropriately. Cut off the power supply in time when not welding. If arc scratches are found, they must be polished with an electric grinding wheel in time. Because on workpieces with corrosion resistance requirements such as stainless steel, arc scars will become the starting point of corrosion and reduce the performance of the material.
Post time: Dec-09-2024